Key Ideas
1. Women played critical roles in the Spanish conquest of the Americas.
2. Women in the Spanish colonies found many ways to challenge and subvert the patriarchy of Spanish colonial society.
3. Indigenous women played a proactive role in tribal responses to Spanish colonization.
4. The cruelties of the encomienda and enslavement systems fell particularly hard on women.
Introduction
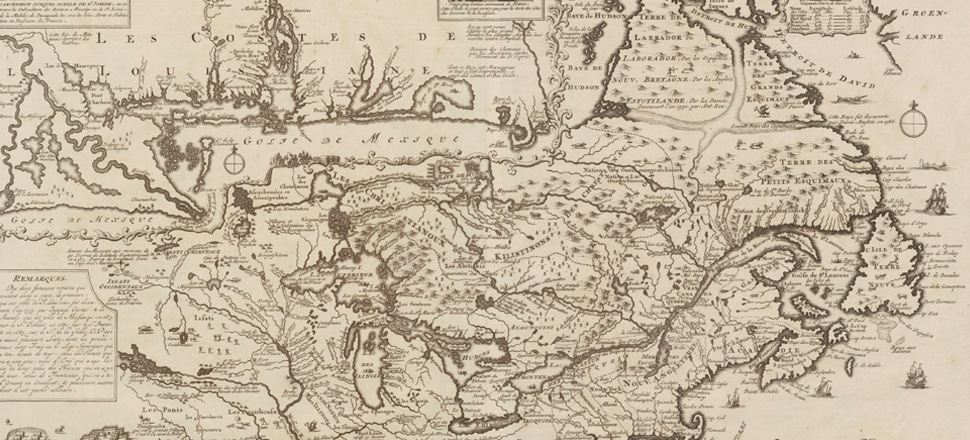
Johann Baptist Homann, Regni Mexicani seu Novæ Hispaniæ, Ludovicianæ, N. Angliæ, Carolinæ, Virginiæ et Pensylvaniæ, necnon insvlarvm archipelagi Mexicani in America Septentrionali, 1759. Library of Congress Geography and Map Division.
Women in the Spanish Colonies, 1492–1715
The popular narrative of the Spanish conquest and colonization of the Americas is hyper-masculine. In the traditional stories, daring male explorers returned to Spain with tales of vast populations and wealth, paving the way for brutal male conquistadors to invade and suppress the Indigenous populations who dared to oppose them. After the early years of invasion, the Spanish established two colonial territories on the mainland: New Spain in North America, and Peru in South America. Spanish elite grew rich off plantations and mines that they staffed with enslaved Indigenous people and Africans, while Catholic missionaries forced thousands of Indigenous people to convert to Catholicism through the oppressive mission system.
What this traditional narrative hides is that women were active participants in every part of the history of the Spanish colonies of the Americas. It was Queen Isabella I of Castile who funded the Columbus voyage of 1492 and who determined the shape and tone of the Spanish conquest. Conquistador Hernán Cortés’s conquest of the Aztec Empire may have failed without the guidance and skill of his enslaved interpreter, Malintzin. Finally, it is impossible to truly understand the horrors of or resistance to the Spanish conquest of the Americas without considering the experiences of Indigenous and African women.
Section Essential Questions
1. What were the rights and responsibilities of women in colonial Spanish society?
2. How did race, class, and social differences affect the lives of the women in the Spanish colonies?
3. How did women contribute to the establishment of new societies in the Spanish colonies in the Americas?
4. What gender-specific challenges did women face in the Spanish colonies?