Key Ideas
1. Women were an integral part of the daily life, culture, and success of New Netherland.
2. Dutch women participated in colonial politics and trade.
3. Free and enslaved Black women in New Netherland had to navigate a challenging and often unclear set of social mores and legal boundaries.
4. Native American women played a proactive role in responses to Dutch colonization.
Introduction
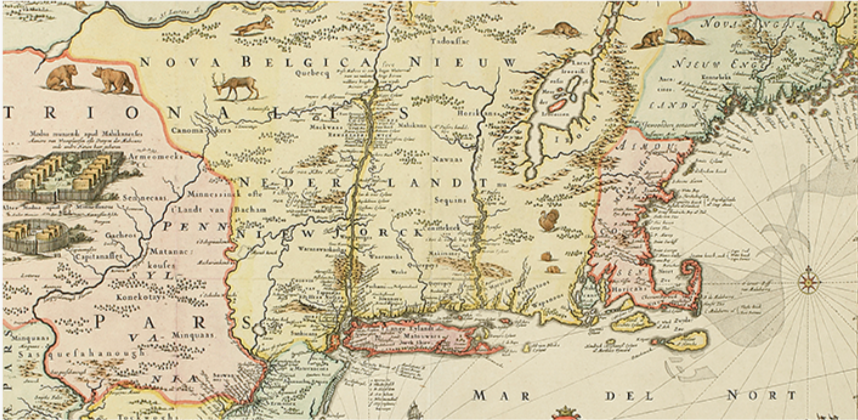
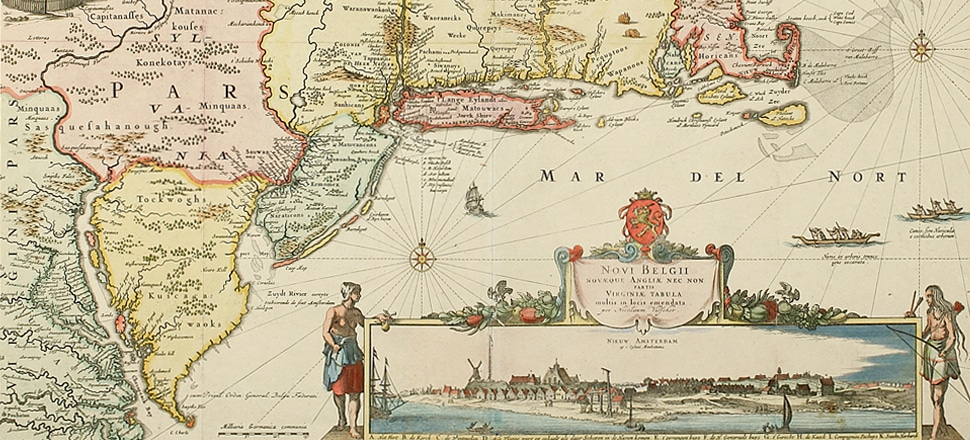
Nicholas Jansz Visscher. Novi Belgii noaeque Angliae nec non partic Virginiae tabula multi in locis emendata, 1682. New-York Historical Society Library.
Women in the Dutch Colonies, 1624–1715
In 1621 the government of the Dutch Republic granted the Dutch West India Company a monopoly over all Dutch trade in the Americas. This was the beginning of an organized Dutch effort to establish colonies and trading posts in North America, South America, and the Caribbean. These new colonies were to be part of the larger Dutch trading empire, which already had trading posts throughout Europe, Africa, and Asia. Women were an integral part of the growth and success of the Dutch colonial empire.
During this time of growth, the colony of New Netherland was born. Under the direct control of the Dutch West India Company, the New Netherland colony covered most of present day New York State, as well as parts of Connecticut, New Jersey, and Delaware. Colonists relied on the rich natural resources in the area to build their settlements. From its foundation in 1624 to its surrender to the English in 1664, the business of New Netherland was business. In New Netherland colonists exchanged European goods for beaver fur with local Native American communities. Traders bought and sold natural resources like lumber that could be used in other parts of the empire. The Atlantic slave trade was also central to the development of the colony.
Section Essential Questions
1. What were the rights and responsibilities of women in colonial Dutch society?
2. How did race, class, and social differences affect the lives of the women in New Netherland?
3. How did women contribute to the establishment and endurance of the economy, society, politics, and culture in New Netherland?
4. What challenges did women face in the Dutch colonies?