Key Ideas
1. The English common law practice of coverture limited the legal and economic opportunities of married women in the English colonies, and English colonial courts actively enforced gender roles and women’s subordination.
2. The knowledge enslaved women brought to the English colonies was critical to the economic success of the colonies.
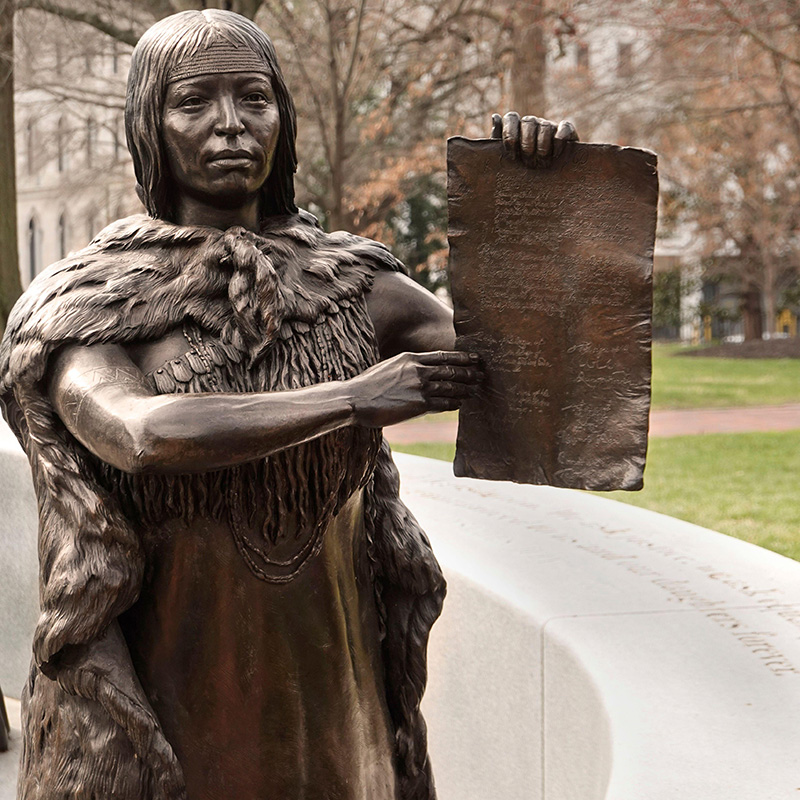
3. Native American women played a proactive role in responses to English colonization.
4. In spite of their legal and cultural limitations, English women in the colonies made important contributions to the Enlightenment.
Introduction
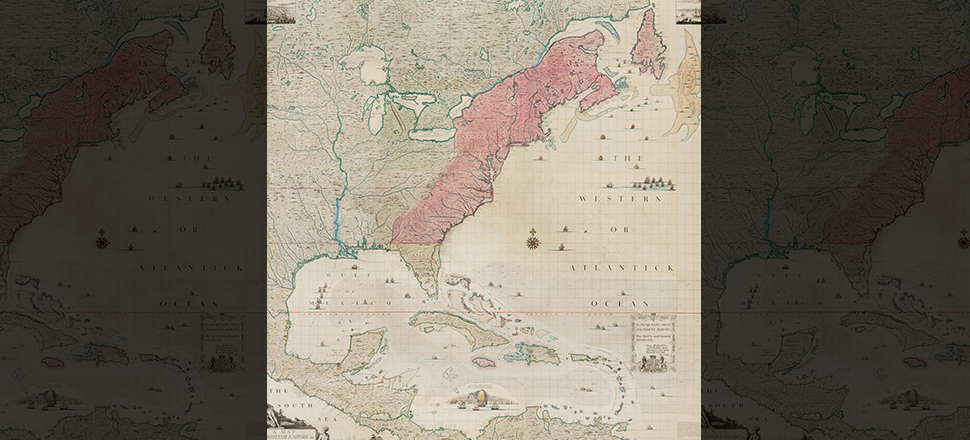
Henry Popple, A map of the British Empire in America with the French and Spanish Settlements adjacent thereto, 1734. New-York Historical Society Library.
Women in the English Colonies, 1607–1715
The history of the early English colonies in North America can be divided into two familiar stories.
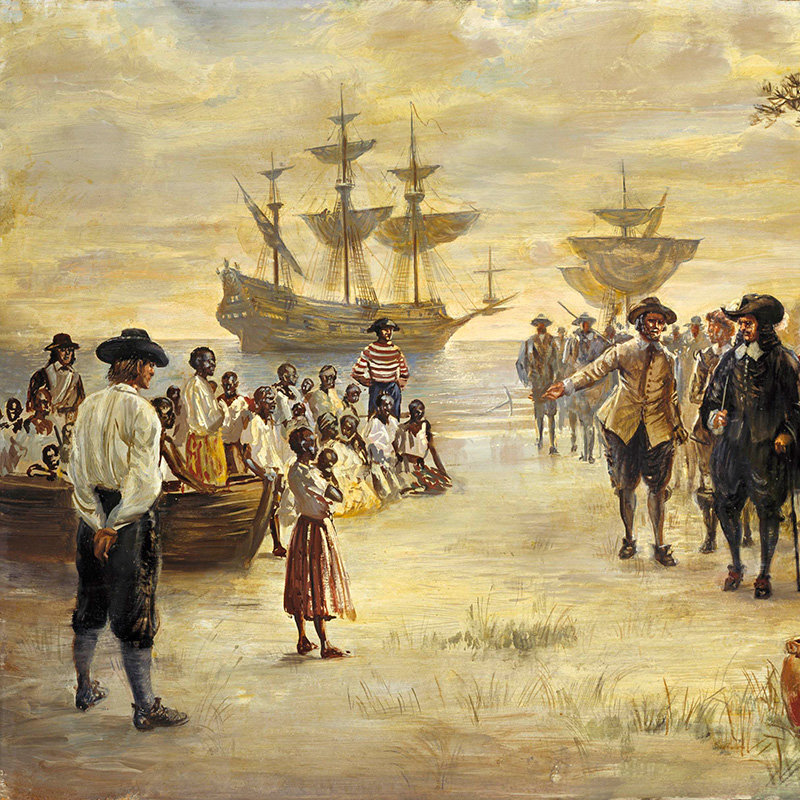
In the southern colonies of Virginia, Maryland, and the Carolinas, the majority of white colonists were indentured servants who worked for a small community of wealthy people who wanted cheap labor to grow tobacco on their plantations. They came hoping to work their way up from servants controlled by masters to independent farmers or merchants. Large numbers of enslaved people were brought to the colonies to supplement the workforce and maximize plantation profits. The pursuit of land for plantations led to the dispossession of the Native American communities that had called the land home for centuries.
In the northern colonies, the area known today as New England, Puritan families settled in small towns. They wanted to build perfect religious communities away from the religious persecution they had lived under in Europe. Indentured servitude and slavery were both widely practiced, but workforces were not concentrated on plantations. Even so, English communities clashed violently with local Native American communities and drove them from their ancestral lands.
Section Essential Questions
1. What roles did women play in colonial England in the 1600s? How did these roles change for women of different races and classes?
2. In what circumstances were women allowed to push the boundaries of their assigned roles? How did they challenge boundaries when it wasn’t “allowed”?
3. How did women contribute to and challenge the establishment of society, politics, the economy, and culture in New England?
4. What gender-specific challenges did women face in the English colonies?