Key Ideas
1. All Americans felt the impact of the Great Depression.
2. Both society and the federal government placed greater value on women’s role in the home during the Depression.
3. Women actively participated in growing bureaucracies, holding leadership positions at the highest levels of government.
4. From managing the home to organizing protests, women worked tirelessly throughout the Depression to ensure daily life continued and Americans received their fair share.
Introduction

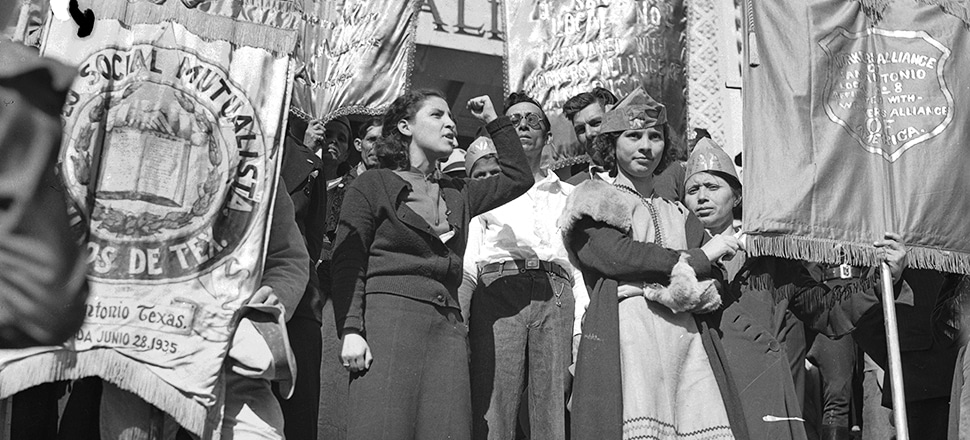
Workers Alliance leader Emma Tenayuca speaking to crowd outside San Antonio City Hall, March 8, 1937. Courtesy, UTSA Special Collections.
The Great Depression
If the Jazz Age propelled American women into the modern world, the Great Depression was a retreat back into the home.
The 1920s offered women the opportunity to celebrate their achievements as voters, consumers, and creative voices. But as the economy crashed and unemployment rose, money dried up and much of the excitement disappeared. The family became the officially recognized and government sanctioned backbone of American society. More than ever, women were expected to roll up their sleeves and keep their homes and families running smoothly – and on a budget. Women without a family – either by choice or by circumstance – were often overlooked.
Local, state, and federal government policies favored men and discouraged married women from entering the workforce. New Deal programs for women relied on sewing and other traditional forms of women’s work.
For more about women during the Great Depression, watch the video below.
This video is from “Women Have Always Worked,” a free massive open online course produced in collaboration with Columbia University.
Section Essential Questions
1. How did the Great Depression change women’s lives?
2. How did the emphasis on married women and domesticity shape women’s experiences during this era?
3. How did women actively contribute to revitalizing the economy and the nation?
4. How did new forms of entertainment, media, and culture shape women’s lives and provide an outlet from the daily toil?