Background
Title IX of the 1972 Education Amendments Act banned discrimination based on sex in educational institutions that received funding from the federal government. The act made it illegal to bar women from academic programs and scholarships, although it is primarily known for its impact on sports. The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) challenged Title IX shortly after it passed. They argued that it should only apply to sports programs that were specifically funded with federal money. Most colleges that received federal funds did not financially support sports programs with government money. They wanted to avoid taking money from popular men’s sports like basketball and football.
The Supreme Court ruled in favor of the NCAA, but Congress passed a law in 1988 that clarified Title IX. Schools had three options to show they complied with Title IX or risk losing their federal funding.
- Participation in men’s and women’s sports was proportional to the student population.
- Program expansion plans to encourage more female students to participate in sports programs.
- Existence of enough opportunities for female students to participate in sports programs to meet their demand.
The requirement to provide equal access to sports programs while in school led to a significant increase in girls’ participation in sports. While only 8% of female high school students were active in sports in 1971, by 1997 that number had increased to 40%. Access to sports while growing up encouraged more girls to pursue professional sports careers. By the 1990s, the first generation of American girls that grew up under Title IX was reaching adulthood. Female athletes competed at the highest levels of sports, including the Olympics and world championships. Cable television increased access to watching them compete. Their success and popularity provided them with lucrative financial opportunities through sponsorships. Their visibility in popular culture and consumer goods subsequently expanded Americans’ views of women’s capabilities.
About the Document
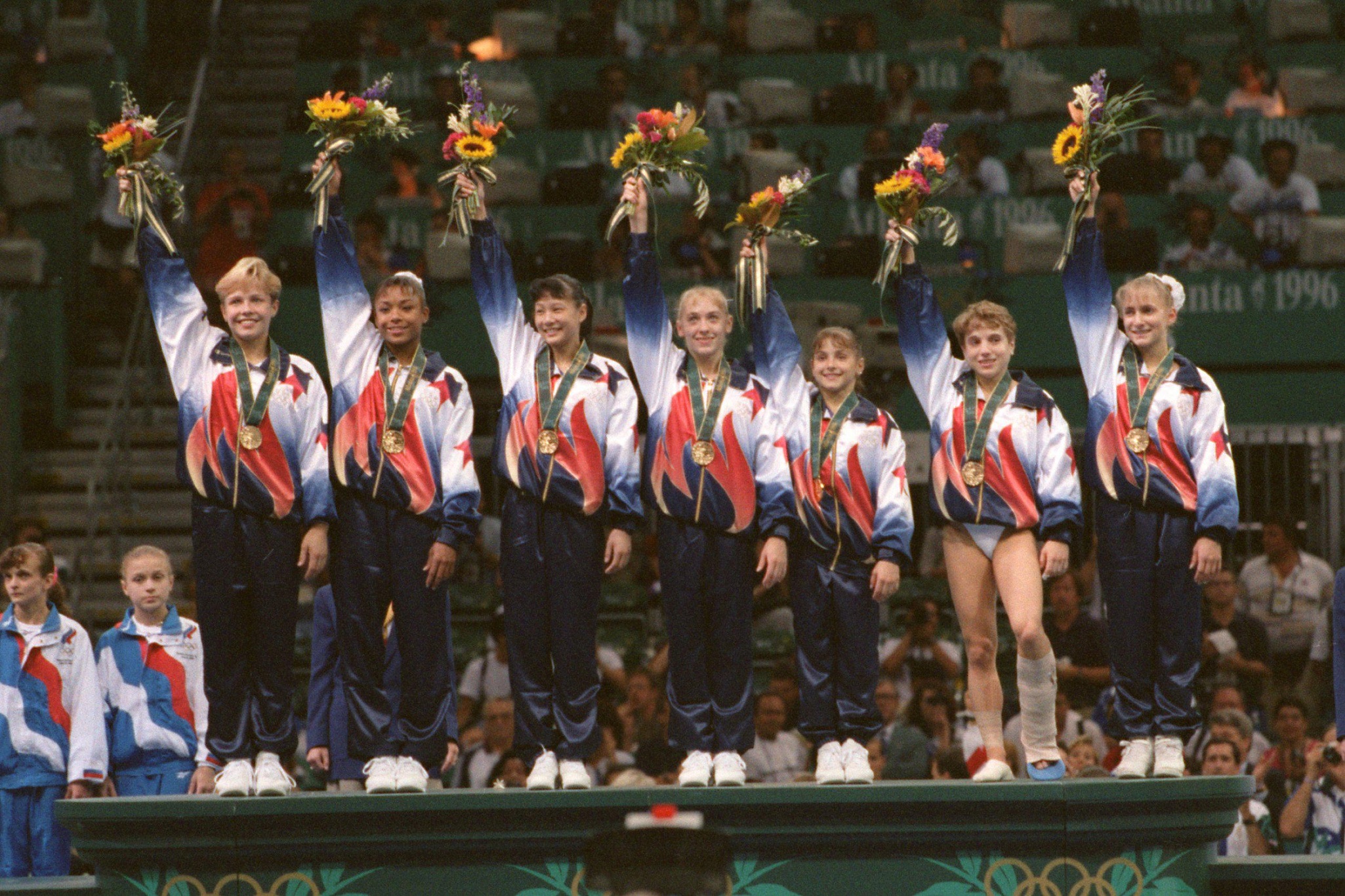
The photograph depicts the American women’s gymnastics team receiving their gold medals at the 1996 Olympic Games in Atlanta. The young athletes, between the ages of 14 and 19, were nicknamed the Magnificent Seven. It was the first team gold medal for the United States in women’s gymnastics, an event that had been dominated by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The photograph includes Dominique Dawes, the first Black American gymnast to win an individual medal at the Olympics. Kerri Strug is wearing a cast after injuring herself during the vault exercise in the competition.
The Newsweek cover shows U.S. soccer player Brandi Chastain celebrating her goal in the 1999 World Cup final against China. It was common for men in soccer to take off their shirts in celebration. When Brandi Chastain did it and exposed her sports bra, it was controversial. FIFA, the international soccer federation, banned the practice for both men and women in 2004.
Discussion Questions
- What effects did Title IX have on women’s sports?
- Why did the NCAA challenge Title IX? How did Congress respond to the Supreme Court decision regarding Title IX?
- What was the significance of the 1996 women’s gymnastics team winning the Olympic gold medal? How did it reflect on tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union during the Cold War, even though it had ended by 1996?
- Why was Brandi Chastain’s celebration controversial? Why do you think Newsweek put the image on their cover? How might girls and women across the country have felt seeing the cover?
Suggested Activities
- In 2021, the differences in women’s and women’s NCAA weight training facilities caused a social media stir. Ask students to consider how women still face inequalities in sports today.
- Read reader’s comments on the Newsweek cover story here. How did the public respond to the cover? Why do you think this Newsweek story only includes positive reactions?
- Pair this resource with the life story of Billie Jean King, an outspoken supporter of Title IX.
- Read the life story of Patsy Mink, the Congresswoman who co-authored Title IX. Congress renamed Title IX the Patsy Takemoto Mink Equal Opportunity in Education Act in 2002.
- Pair this resource with the life story of Ann Bancroft, an explorer who was able to use Title IX to play sports in high school.
- Consider the impacts of the federal government on women’s rights during this time period by combining this resource with U.S. v. Virginia and Nursing Relief Act.
Themes
ACTIVISM AND SOCIAL CHANGE; AMERICAN CULTURE; WORK, LABOR, AND ECONOMY