Elizabeth Cochran was born on May 5, 1864 in Cochran’s Mills, Pennsylvania. The town was founded by her father, Judge Michael Cochran. Elizabeth had fourteen siblings. Her father had ten children from his first marriage and five children from his second marriage to Elizabeth’s mother, Mary Jane Kennedy.
Michael Cochran’s rise from mill worker to mill owner to judge meant his family lived very comfortably. Unfortunately, he died when Elizabeth was only six years old and his fortune was divided among his many children, leaving Elizabeth’s mother and her children with a small fraction of the wealth they once enjoyed. Elizabeth’s mother soon remarried, but quickly divorced her second husband because of abuse, and relocated the family to Pittsburgh.
Elizabeth knew that she would need to support herself financially. At the age of 15, she enrolled in the State Normal School in Indiana, Pennsylvania, and an added an “e” to her last name to sound more distinguished. Her plan was to graduate and find a position as a teacher. However, after only a year and a half, Elizabeth ran out of money and could no longer afford the tuition. She moved back to Pittsburgh to help her mother run a boarding house.
In 1885, Elizabeth read an article in the Pittsburgh Dispatch that argued a woman’s place was in the home, “to be a helpmate to a man.” She strongly disagreed with this opinion and sent an angry letter to the editor anonymously signed “Lonely Orphan Girl.”
The newspaper’s editor, George A. Madden, was so impressed with the letter that he published a note asking the “Lonely Orphan Girl” to reveal her name. Elizabeth marched into the Dispatch offices and introduced herself. Madden immediately offered her a job as a columnist. Shortly after her first article was published, Elizabeth changed her pseudonym from “Lonely Orphan Girl” to “Nellie Bly,” after a popular song.
Elizabeth positioned herself as an investigative reporter. She went undercover at a factory where she experienced unsafe working conditions, poor wages, and long hours. Her honest reporting about the horrors of workers’ lives attracted negative attention from local factory owners. Elizabeth’s boss did not want to anger Pittsburgh’s elite and quickly reassigned her as a society columnist.
To escape writing about women’s issues on the society page, Elizabeth volunteered to travel to Mexico. She lived there as an international correspondent for the Dispatch for six months. When she returned, she was again assigned to the society page and promptly quit in protest.
Elizabeth hoped the massive newspaper industry of New York City would be more open-minded to a female journalist and left Pittsburgh. Although several newspapers turned down her application because she was a woman, she was eventually given the opportunity to write for Joseph Pulitzer’s New York World.
In her first act of “stunt” journalism for the World, Elizabeth pretended to be mentally ill and arranged to be a patient at New York’s insane asylum for the poor, Blackwell’s Island. For ten days Elizabeth experienced the physical and mental abuses suffered by patients.
Elizabeth’s report about Blackwell’s Island earned her a permanent position as an investigative journalist for the World. She published her articles in a book titled 10 Days in A Mad House. In it, she explained that New York City invested more money into care for the mentally ill after her articles were published. She was satisfied to know that her work led to change.
Activist journalists like Elizabeth—commonly known as muckrakers—were an important part of reform movements. Elizabeth’s investigations brought attention to inequalities and often motivated others to take action. She uncovered the abuse of women by male police officers, identified an employment agency that was stealing from immigrants, and exposed corrupt politicians. She also interviewed influential and controversial figures, including Emma Goldman in 1893.
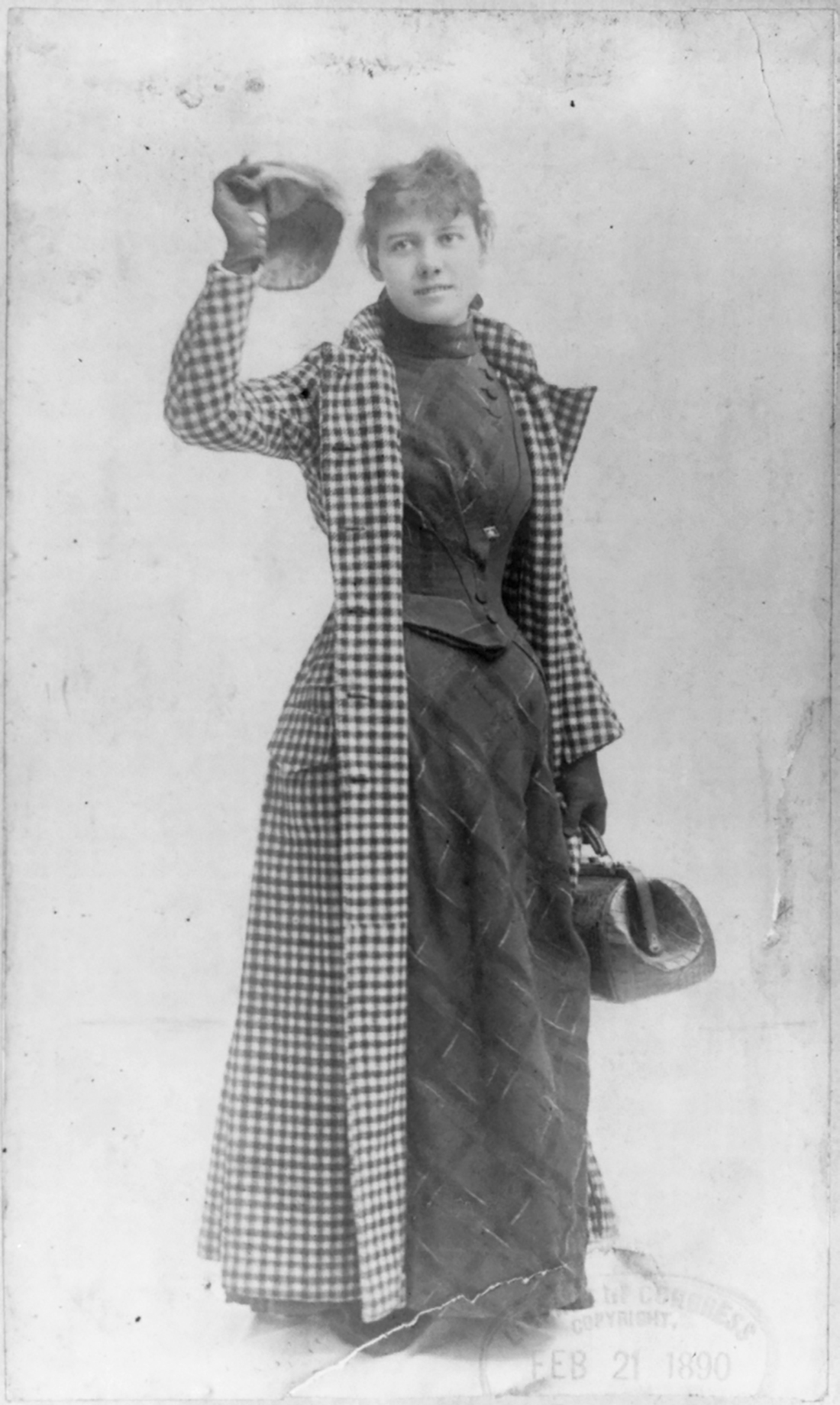
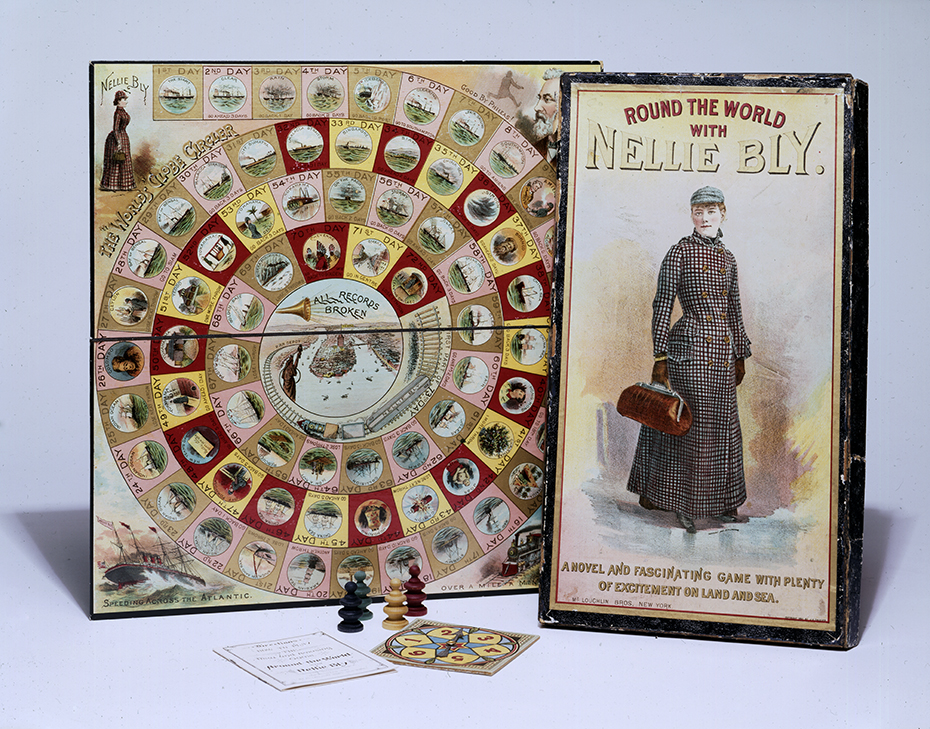
The most famous of Elizabeth’s stunts was her successful seventy-two-day trip around the world in 1889, for which she had two goals. First, she wanted to beat the record set in the popular fictional world tour from Jules Verne’s Around the World in Eighty Days. Second, she wanted to prove that women were capable of traveling just as well as—if not better than—men. Elizabeth traveled light, taking only the dress she wore, a cape, and a small traveler’s bag. She challenged the stereotypical assumption that women could not travel without many suitcases, outfit changes, and vanity items. Her world tour made her a celebrity. After her return, she toured the country as a lecturer. Her image was used on everything from playing cards to board games. She recounted her adventures in her final book, Around the World in 72 Days.
Activist journalists like Elizabeth—commonly known as muckrakers—were an important part of reform movements.
In 1895, Elizabeth retired from writing and married Robert Livingston Seaman. Robert was a millionaire who owned the Iron Clad Manufacturing Company and the American Steel Barrel Company. When Robert died in 1904, Elizabeth briefly took over as president of his companies.
In 1911, she returned to journalism as a reporter for the New York Evening Journal. She covered a number of national news stories, including the Woman Suffrage Parade of 1913 in Washington, D.C. Elizabeth often referred to suffrage in her articles, arguing that women were as capable as men in all things. During World War I, she traveled to Europe as the first woman to report from the trenches on the front line.
Although Elizabeth never regained the level of stardom she experienced after her trip around the world, she continued to use her writing to shed light on issues of the day. She died of pneumonia on January 27, 1922.
Vocabulary
- boarding house: A house where people rent bedrooms in which to live.
- front line: the place where the fighting takes place in a war; also known as a battle line.
- investigative: Closely studying and researching.
- muckrakers: Activist journalists who wrote about the problems in society with the goal of motivating readers to take action.
- society page: The part of a newspaper that focuses on social news, including gossip and cultural events.
- stunt journalism: Journalism that includes the writer participating in some kind of unexpected and fantastic act.
- suffrage: The right of voting; in this era, suffrage often referred specifically to woman suffrage, or the right of women to vote.
- tuition: The fee paid to a school.
Discussion Questions
- Elizabeth is often described as a muckraker. What does that mean, and how did her writing contribute to reform efforts on a variety of issues?
- How might Elizabeth’s position as a woman have helped her investigative reporting? What might she have been able to do that men could not?
- To what extent did Elizabeth’s trip around the world redefine ideas of what it meant to be a woman?
Suggested Activities
- Combine Elizabeth Cochrane’s life story with the life stories of Ida B. Wells, Jovita Idar, and Edith Maude Eaton, all of whom used a career in journalism to advocate for social reform.
- Connect Elizabeth Cochrane’s work to that of fellow muckraker Lewis Hine, who used photography to shed light on the challenges of life in modern industrial America.
- Elizabeth Cochrane was one of many Americans who fought to eradicate what she perceived as the evils of modern life. Conduct a close examination of the “Woman’s Sphere” illustration from Life Magazine, which illustrates some of the evils middle-class Americans feared.
Themes
ACTIVISM AND SOCIAL CHANGE; AMERICAN IDENTITY AND CITIZENSHIP