Background
Although the Thirteenth Amendment abolished slavery and involuntary servitude, it included an exception for prisoners. Following the Civil War, convict labor was a major source of income for many state governments in the South. States could force prisoners to work for private citizens, who would pay the state for the prisoners’ labor. This was called the convict lease system.
The convict lease system was particularly important to the continuation of the Southern plantation system. After the war, plantation owners struggled to find enough workers, particularly workers who they could easily control. The political leadership of the South was made up by white men, most of whom were former enslavers who still ran plantations. They exploited their political power to secure prison labor on their plantations.
Georgia abolished the convict lease system in 1908.
About the Image
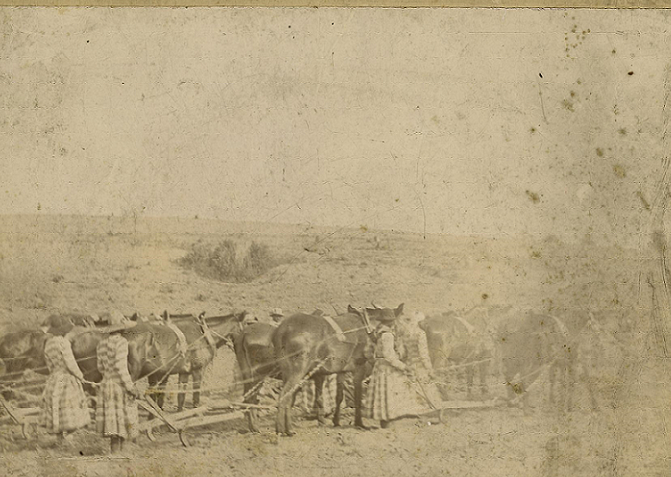
The Georgia prison system forced women prisoners to work just like male prisoners. However, imprisoned white women were regularly exempt from this labor. This meant that almost all of the women prisoners forced into labor in Georgia were Black. Black women prisoners had to work in domestic service, skilled labor, and agriculture roles. Those who did not have specific skills and those considered unruly ended up working on the state farm, which was the most physically challenging.
The photograph shows Black women prisoners plowing a field at the Georgia state penitentiary in Milledgeville. The women produced various crops for use in the prison system, including cotton for clothing and food, such as corn and sweet potatoes, to feed the prisoners. They worked long hours in a hot climate, and the prison guards were verbally and physically abusive.
Vocabulary
- lease: To rent out.
- penitentiary: A state or federal prison in the United States.
Discussion Questions
- What types of work did Black women do in prison? What conditions did they work in?
- Why did Georgia implement the convict lease system? How did it affect Black women?
- What were Black Codes and how were they connected to the convict lease system?
Suggested Activities
- APUSH Connection: 6.4: The “New South”
- Read The Reason Why, in which Ida B. Wells speaks out against the treatment of Black women in the prison system.
- Compare the conditions in the Georgia prison system to those in a New Jersey prison. What differences and similarities are there between the descriptions?
- For a larger lesson on the experiences of Black women during this time period, combine this resource with a study on Black domestic workers, an article about a labor strike in Atlanta, images of Exodusters, Ida B. Wells’s pamphlet about Jim Crow, a speech from the first Black women’s club convention, an Aunt Jemima advertisement, and the life stories of Lucy Parsons, Josephine St. Pierre Ruffin, Edmonia Lewis, and Mary Ellen Pleasant.
Themes
WORK, LABOR, AND ECONOMY
New-York Historical Society Curriculum Library Connections
- For more resources relating to Black experiences under Jim Crow, see our curriculum guide Black Citizenship in the Age of Jim Crow.