Key Ideas
- Immigration and migration significantly affected the experiences of women in the workplace.
- Industrialization changed the lives of women of different races and socioeconomic classes in different ways.
- Women activists from different backgrounds fought for better working conditions through various means.
Introduction
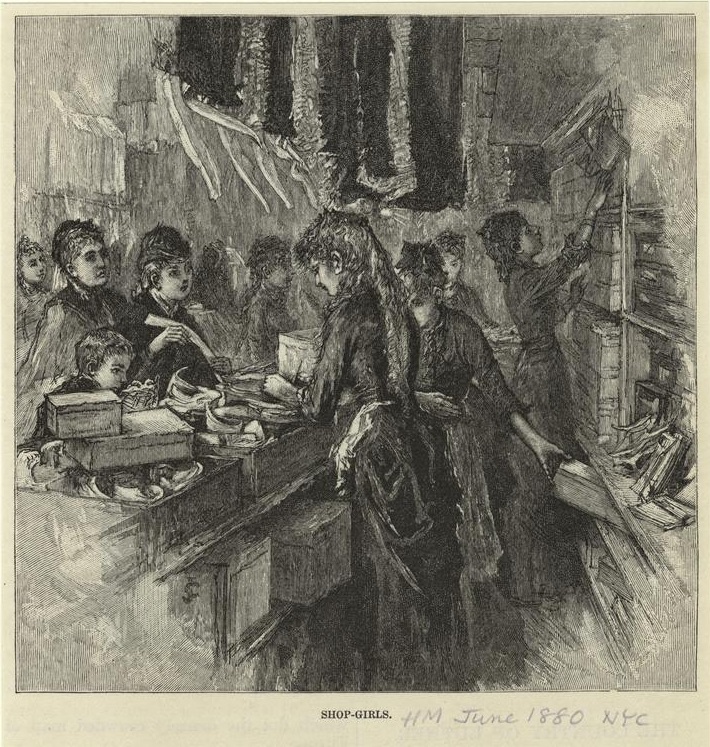

The Miriam and Ira D. Wallach Division of Art, Prints and Photographs: Picture Collection, The New York Public Library. “Shop-Girls.” The New York Public Library Digital Collections. 1880. https://digitalcollections.nypl.org/items/510d47e1-05d5-a3d9-e040-e00a18064a99
Labor and Industry
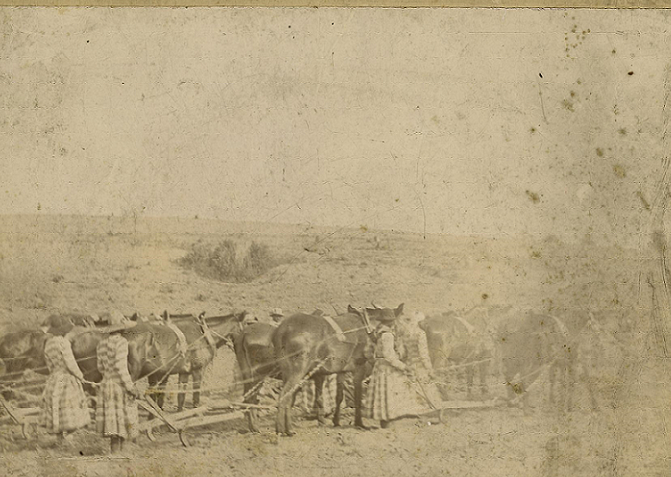
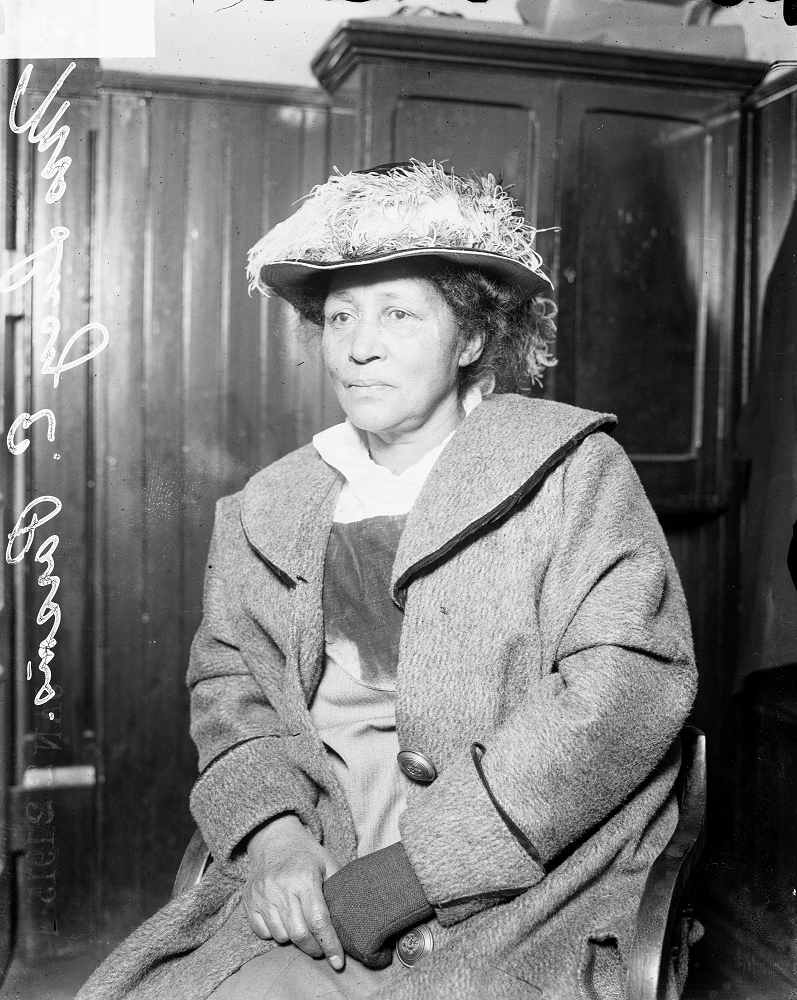
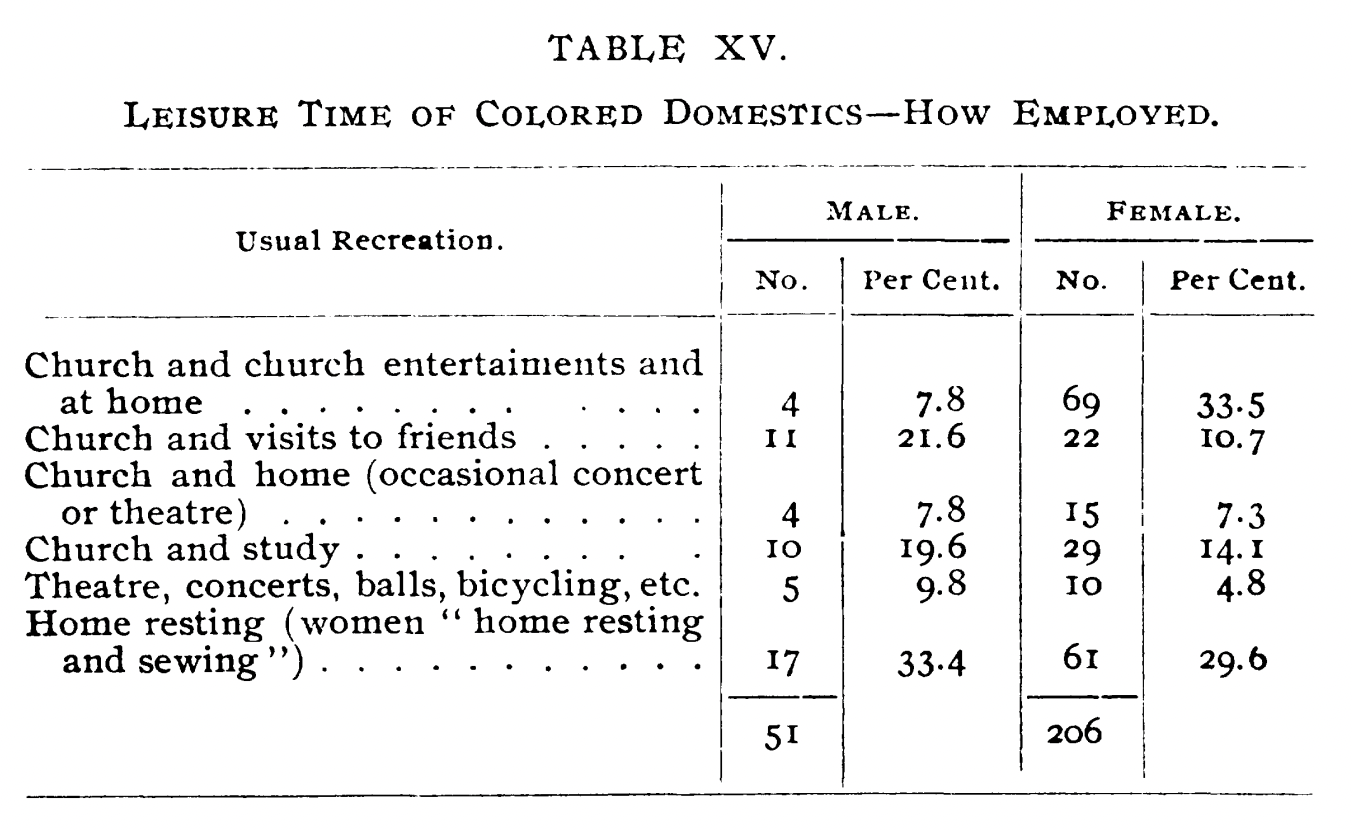
The decades following the Civil War saw a major movement of people within the United States and from abroad. Many formerly enslaved people migrated to the North for new job opportunities. Millions of European immigrants moved to the United States, seeking work in the growing American economy. Labor within the workplace was segregated, which led to tensions between Black and white workers.
The industrialization of the United States moved the country from an agricultural to an industrial economy. The agricultural labor that was still performed in the South predominantly relied on the work of Black Americans. Cities developed as the main centers for production. Factory workers faced subpar working conditions. Activists reported on the realities of the industrial workplace and some advocated for radical changes in the American economy. The highest social classes lived in excess and were criticized as disparities between the rich and poor increased.
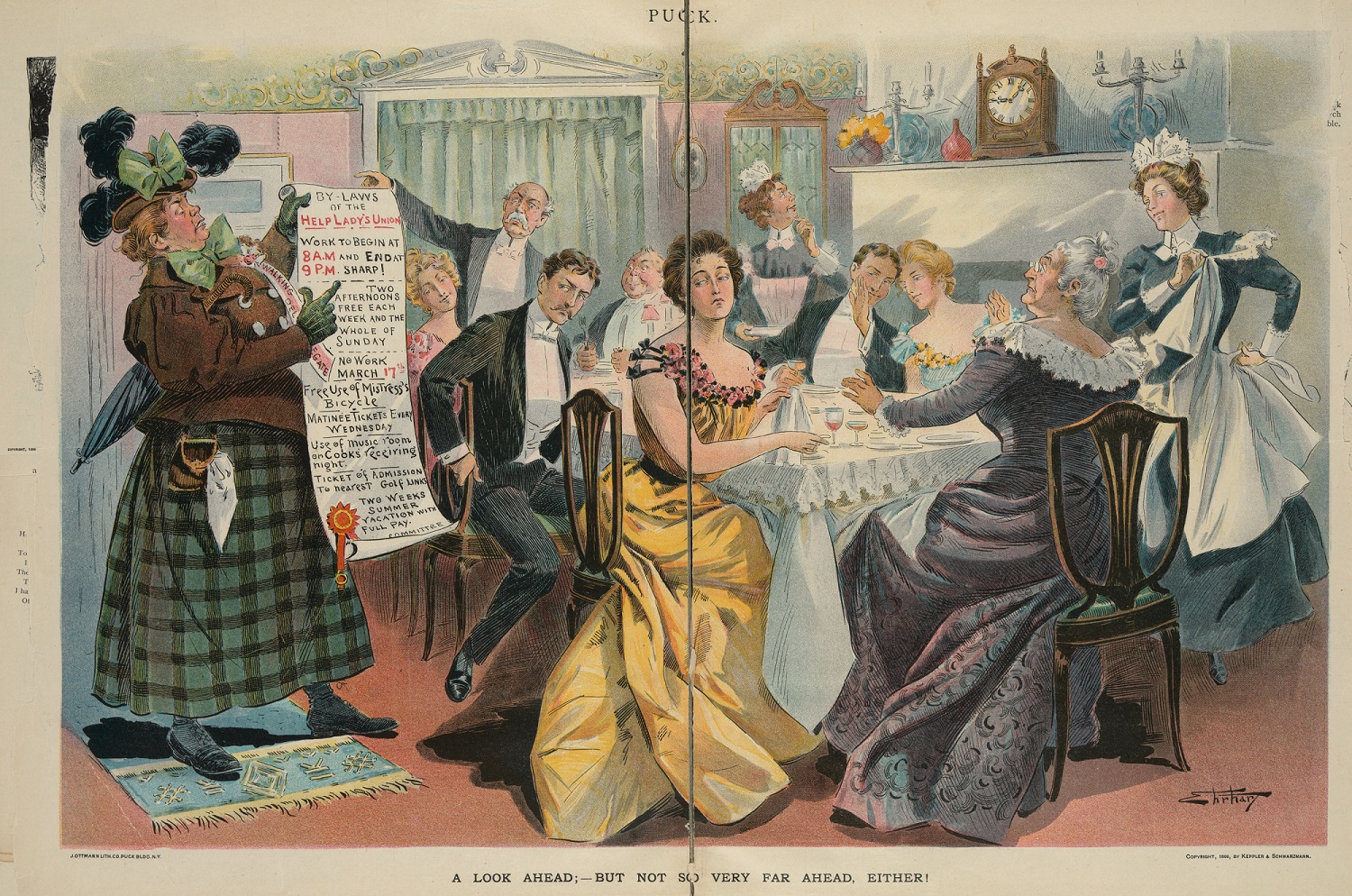
The primary responsibility of women in the expanding middle class was to serve as wives and mothers. The growth of consumerism provided them with a new role as consumers, as they were responsible for purchasing items for their homes and families. Advertising for household goods was aimed at middle-class women and often promised to make household responsibilities, and their lives, easier.
Section Essential Questions
- How did industrialization affect women from different backgrounds? How did race and class influence the challenges and opportunities available to women?
- How did women from different racial and class backgrounds become active in labor reform? What did they do?
- Why did women choose to immigrate or migrate?
- How did wealth disparity during the Gilded Age affect women?