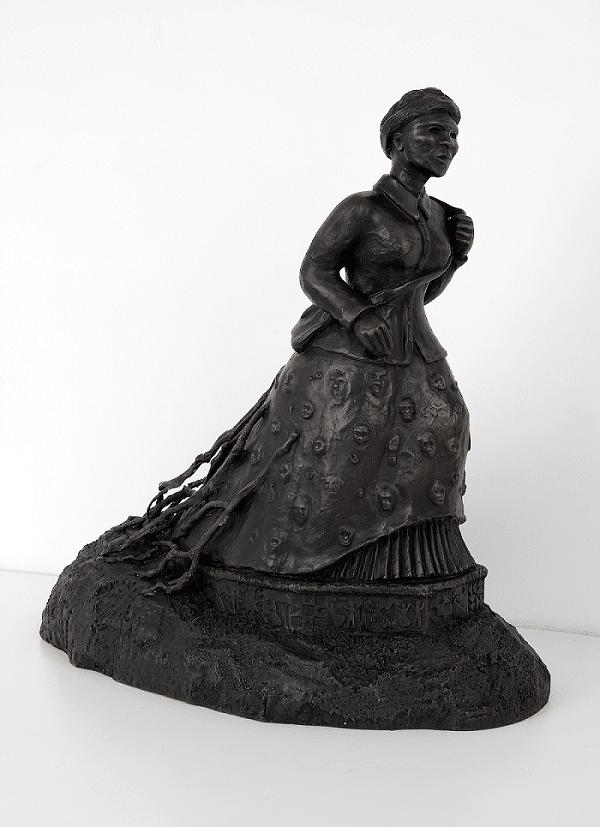
Harriet Tubman was born around the year 1820 in Dorchester County, Maryland. Her parents named her Araminta Ross. Her mother, Harriet Green, was an enslaved woman owned by Mary Pattinson Brodess. Her father, Ben Ross, was an enslaved man owned by Anthony Thompson. They were brought together when Mary and Anthony got married. Ben and Harriet had nine children.
Araminta inherited the status of enslaved person from her mother. She was put to work around the age of five. When she was young, her enslaver’s son sold three of Araminta’s sisters to distant plantations, breaking up her family. Araminta’s mother fought successfully to keep the rest of her children with her, but Araminta learned as a child that her life would never be secure so long as she was enslaved.
Araminta suffered violence at the hands of her enslavers and other white people in her community. Her body was scarred from beatings. When she was a teenager, an overseer in town hit her in the head with a two-pound weight. Because of this attack, Araminta suffered from seizures, severe headaches, and narcolepsy for the rest of her life.
Araminta married John Tubman, a local free Black man, in 1844. The marriage did not change her legal status and she remained enslaved. Around the time of her marriage, she took the name Harriet, probably in honor of her mother. In 1849, she learned that her enslaver was planning to sell her. She decided to take her own freedom rather than submit. John did not join her and eventually remarried. Her brothers set off with her but grew frightened and returned to the plantation. Harriet continued on her own. She was aided by abolitionists who belonged to the Underground Railroad network. When she reached Philadelphia, in the free state of Pennsylvania, she found a job and started a new life.
Harriet’s fame spread throughout the country, and she began to speak at abolitionist events. At the height of her fame, governments in the South offered rewards totaling $40,000 for her capture.
In 1850, Harriet learned that her niece Kessiah was going to be sold. She traveled back to Maryland and helped Kessiah and her family escape to Philadelphia. This was the first of 19 trips Harriet made to guide her family, friends, and anyone else who wanted to use the Underground Railroad to take their own freedom. After the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 made it impossible for escaped slaves to live safely in Northern states, Harriet changed her route and brought people all the way to Canada.
Harriet was militant in her approach to guiding people on the Underground Railroad. She carried a gun and threatened to kill any person who wanted to turn back and endanger the group. She used a tonic to put babies into a deep sleep, so their cries would not draw attention during nighttime travels. She is estimated to have saved about 70 to 80 people, including her elderly parents. Her fame spread throughout the country, and she began to speak at abolitionist events. At the height of her fame, governments in the South offered rewards totaling $40,000 for her capture. Militant abolitionist John Brown admired her greatly. He called her “General Tubman” and consulted with her before conducting his raid on Harper’s Ferry. Harriet and John both believed that extreme acts were necessary to end slavery in the United States.
When the Civil War broke out in 1861, Harriet focused her efforts on supporting the Union Army. She was assigned to the 2nd South Carolina Colored Troops under Colonel James Montgomery. She was given the jobs of cook and nurse because of her race and sex, but Harriet was soon performing more militaristic duties. Her knowledge of the local terrain and her Underground Railroad contacts made her an ideal spy. Her race and sex made it easy for her to slip behind Confederate lines to gather information. She did not abandon her efforts to help enslaved people—she helped the enslaved people who escaped during the war find shelter and safety. But despite all of her work, Harriet was paid very little. She supplemented her income by selling baked goods to Union soldiers.
On June 2, 1863, Harriet became the first woman to lead Union troops into battle. Based on information she had gathered, she led a group of Colonel Montgomery’s troops in a raid down the Combahee River. They destroyed Confederate Army ammunition depots and storage houses and burned several large plantations. They liberated 750 people from slavery in a single night.
When the war ended, Harriet settled in Auburn, New York, on land she had purchased before the war. Her parents and family were already living there. In 1868, she applied for a military pension but was denied, although Black male spies and soldiers received them. In 1869, she married a Black Civil War veteran named Nelson Davis, and in 1874, they adopted a baby girl named Gertie. It was only after Nelson’s death in 1888 that Harriet began to receive a widow’s pension from the government.
Harriet remained politically active after the war. She joined Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton in their campaign for women’s rights. She attended the founding meeting of the National Association of Colored Women in 1896, where she met and supported Ida B. Wells. Yet Harriet never had enough money to live comfortably. In 1898, she petitioned the government for her military pension and back pay, but instead they increased her widow’s pension from $8 to $20 a month.
Harriet never stopped working to improve her community and country. In 1908, she opened the Tubman Home for Aged and Indigent Negroes, a charity home that she hoped would carry on her work after her death. She died there in 1913 surrounded by friends and family.
Vocabulary
- abolitionist: A person who fought to end slavery in the United States.
- ammunition: Explosive items used by the military.
- Confederate: Relating to the group of states that seceded from the United States before the Civil War in order to preserve slavery.
- contraband: The name the Union Army gave to all enslaved people who were liberated or escaped to Union lines during the American Civil War.
- Fugitive Slave Act of 1850: A law that required Northern states to return runaway enslaved people to their enslavers.
- narcolepsy: A condition that causes a person to fall into a deep sleep without warning.
- overseer: A person who was in charge of supervising the work of enslaved people.
- pension: A sum of money regularly paid to a former soldier for life in recognition of their service.
- Underground Railroad: A network of safe houses that helped enslaved people travel to freedom.
- Union: The name for the states that remained a part of the United State during the Civil War.
Discussion Questions
- How did Harriet Tubman’s childhood affect her choices as an adult?
- What extreme actions did Harriet Tubman take to dismantle slavery in the United States?
- How did Harriet support the Union war effort? What recognition did she receive for her actions?
- How did Harriet Tubman’s race and sex affect her opportunities in life?
Suggested Activities
- APUSH Connection: 5.8 Military Conflict in the Civil War
- Harriet Tubman existed at an intersection of a variety of oppressed identities: Black, woman, poor, and dis/abled. Be sure to highlight each of these aspects of her identity when teaching her story.
- After reading this life story, invite students to read the record of Harriet Tubman’s recollections of her early work guiding people to freedom. Why are all the sources we have on her life second hand? How does this complicate learning her story?
- Most biographies of Harriet Tubman minimize her role in the American Civil War. Ask students to consider why this might be the case, and why it is important to include this part of her story. Use this life story to move students beyond the typical narrative of Harriet Tubman’s life and legacy.
- Invite students to watch the film Harriet and consider how filmmakers adapted Harriet Tubman’s life for the big screen. What changes did they make? What do these choices reveal?
- Invite students to research the story of John Brown and write an essay considering why he and Harriet Tubman admired each other’s approach to abolition.
- To learn more about Black women’s role in the post-Civil War fight for women’s rights, visit “All Bound Up Together.”
- Harriet Tubman dedicated her final years to provide a safe home for her family and vulnerable members of her community. To learn more about Black women’s role in post-war community-building, read Life Story: Louisa Smith, Information Wanted, Life Story: Matilda Hughes, and Life Story: Elizabeth Keckley.
- Harriet Tubman was one of many Black women abolitionists operating in the antebellum period. After reading this story, invite students to learn more about the experience of Black women anti-slavery activists in the antebellum period, and compare the challenges and experiences of each: Elizabeth Jennings, Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl, Salem Female Anti-Slavery Society, Resistance, Harriet Robinson Scott, and Sojourner Truth.
- Harriet Tubman’s story illustrates one way women could take an active role in the American Civil War. For a larger lesson on this topic, teach this life story together with any of the following: Nursing, Women’s War Production, Sanitary Fairs, Smuggling, and Women Soldiers.
Themes
ACTIVISM AND SOCIAL CHANGE; POWER AND POLITICS
New-York Historical Society Curriculum Library Connections
- For more about the effects of the Fugitive Slave Law, see New York Divided.
- For more about Black Americans’ experiences after the Civil War, explore Black Citizenship in the Age of Jim Crow.